Why isn't Wi-Fi working on my Windows PC?
Wi-Fi connection problems - is one of the most common challenges faced by users of the Windows operating system. Whether you're running Windows 10 or the latest version of Windows 11, a lost internet connection can interfere with your work, education or entertainment. In this article, we'll discuss the most common causes of Wi-Fi not working and provide a detailed step-by-step guide on how to fix the problem.
Common Wi-Fi problems on computers running Windows operating systems
Before we get to the solutions, it's important to understand the main reasons why your computer may not be connecting to a Wi-Fi network:
- Drivers that don't work or are out of date
If the network adapter driver (NDA) does not have a driver for the network adapter, you can use the following options. drivers) are out of date or corrupted, your computer may not be able to detect or connect to the network. - Incorrect network settings
Sometimes inadvertently changed network settings or corrupted configuration files can cause problems. - Problems with your router
Wi-Fi outages may not be caused by your computer, but by your router or internet service provider. - Impact of Windows updates
New operating system updates sometimes cause incompatibility with network devices. - Physical faults in the Wi-Fi adapter
If you're using an older computer, the Wi-Fi module's hardware may be damaged.
How do I fix Wi-Fi problems on Windows?
Here are some steps to help you restore a stable Wi-Fi connection:
1. Check that Wi-Fi is switched on
Although it may seem simple, the problem is often caused by disabled Wi-Fi:
- Windows 10/11: Click on the network icon in the taskbar and make sure the Wi-Fi button is on.
- Some laptops have a physical Wi-Fi switch - check if it's active.

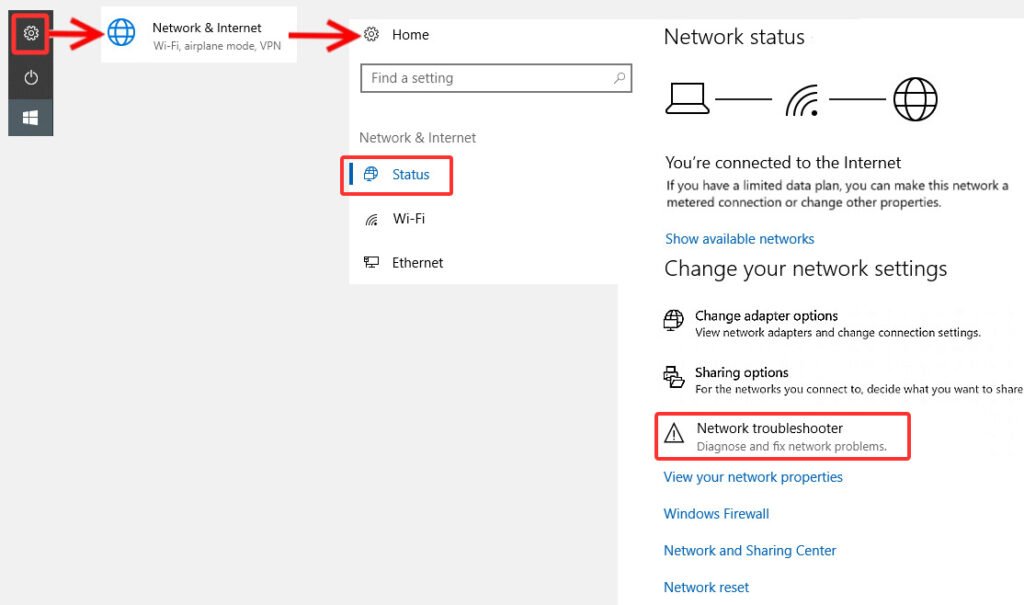
2. Start Network Troubleshooter„
Windows has a built-in tool for solving network problems:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot.
- Choose Internet Connections and click Run the Troubleshooter.
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
3. Update or reinstall drivers
Outdated drivers are one of the main causes of Wi-Fi problems.
- Right-click Start menu and select Device Manager.
- Find Network Adapters and click on the name of your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Choose Update Driver and let Windows automatically search for updates.
If that doesn't work, try it:
- Choose Uninstall Device, then restart your computer - Windows will automatically install the missing driver.
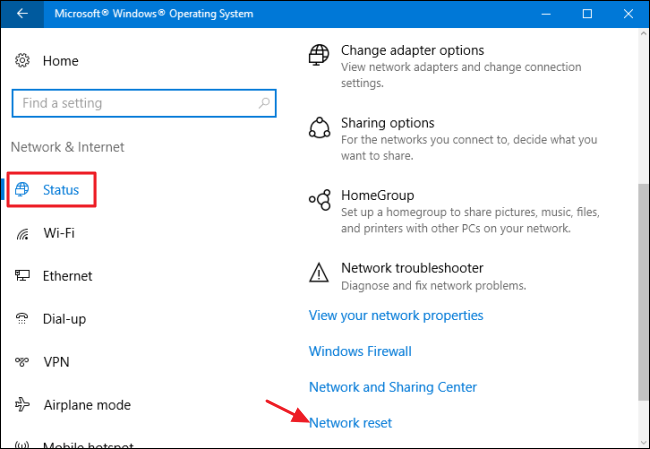
4. Restart your network settings
If the network problem persists, you can perform a full reset of your network settings:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Click Network reset and confirm the action.
- After restarting your computer, re-enter your Wi-Fi password.
5. Check your router
If none of the above solutions work, the problem may lie with your router:
- Make sure all cables are connected properly.
- Reboot the router by unplugging it from the mains for 10-15 seconds.
- Check that other devices (e.g. phones) can connect to the same Wi-Fi network.

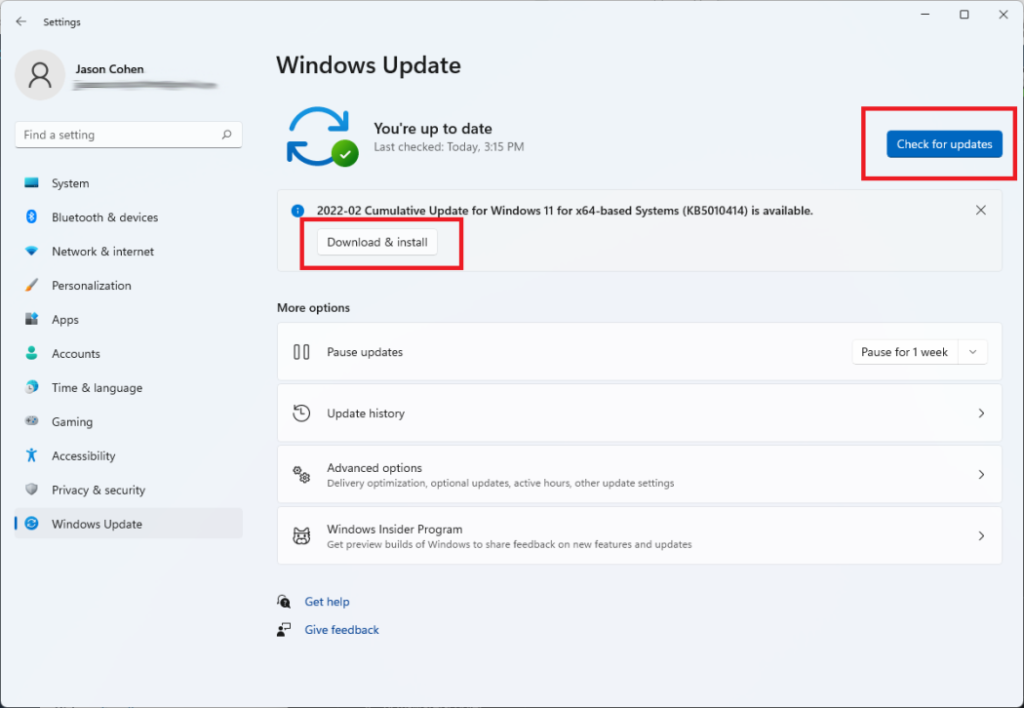
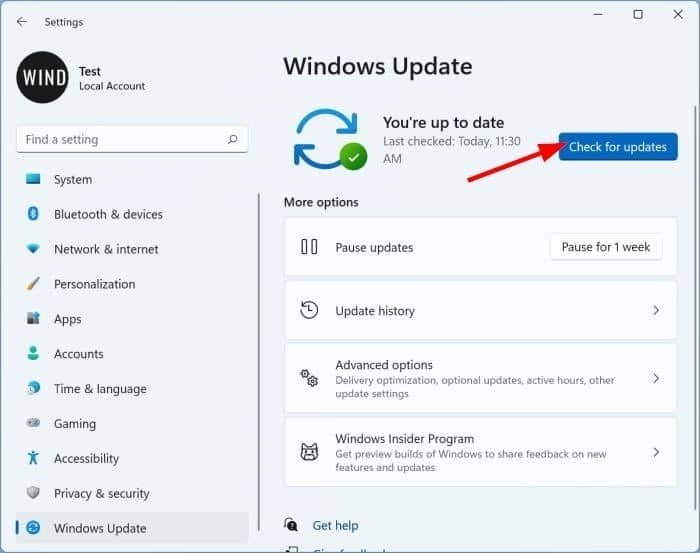
6. Check for Windows updates
Recent updates may fix bugs or add missing features:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Check for pending updates and install them.
7. Additional solutions
- Use an alternative network: if your computer has an Ethernet connection, connect directly via cable.
- Consider replacing the Wi-Fi module if you are using an older computer.
When to seek professional advice?
If you've tried all the solutions and the Wi-Fi still doesn't work, the problem may be more serious (e.g. faulty hardware). In this case, we recommend you contact a technical support specialist.
Finally,
Wi-Fi connection problems can be frustrating, but in most cases they can be solved using the methods above. If you're running an older version of Windows, consider upgrading to Windows 10 or Windows 11, which can improve system compatibility and stability.
You can find out more about Windows operating systems in our In the Windows operating systems category.